Behind every loan approval, mortgage, or business credit line lies a single defining factor: the quality of your credit decisioning process. Whether your company focuses on B2B financing, consumer loans, or mortgage lending, the foundation is the same—a structured approach to credit decisions.
In this article, you’ll learn how the credit decision-making process works, its key stages, the common pitfalls lenders face, and how to overcome them.
Key Takeaways
- Credit decisioning is only as strong as its data, models, and governance. Outdated systems and narrow data sources create hidden risk.
- Effective credit decisions rely on three core stages: data gathering, risk analysis, and consistent, decision-making.
- Overreliance on manual overrides slows decisions and increases bias, while hybrid automation improves speed, consistency, and traceability.
What Is Credit Decisioning?
Credit decisioning is the process companies use to evaluate and establish the creditworthiness of a client or customer. It includes financial track record, payment patterns, economic stability, and financial health, which collectively allow companies to reduce default risk and increase approval speed.
An effective credit decisioning process ensures that businesses can confidently extend credit to their clients and customers, knowing they are financially stable and reliable. As a result, it helps companies to mitigate risks of non-payment, advance cash flow, and maintain customer satisfaction.
7 Key Factors To Evaluate Before Making Credit Decisions
Credit decisioning is a complicated process that consists of different stages. But there are also several factors to consider in this process to make it effective:

- Payment behavior: Scrutinize the client’s payment patterns to find out whether they have had any problems with late or missed payments.
- Credit history: Carefully look through the customer’s previous credit behavior, such as payment punctuality, bankruptcies, or defaults.
- Industry risk: As some industries can be more prone to instability, meticulously evaluate the client’s industry before making a decision.
- Financial statements: Review the client’s balance sheets, income, and cash flow statements to evaluate their financial health.
- Credit score: Use credit scores from major bureaus to assess customer creditworthiness.
- Economic conditions: Assess the wider economic climate and its potential effect on the client’s capability to pay.
- Collateral: Examine the assets or guarantees the customer may provide to secure the credit.
What Are the 5 Cs of the Credit Decision?
As mentioned before, the credit decision-making process requires utmost attention. To make it more understandable how to estimate a client’s creditworthiness, there is the framework of the 5 Cs. By carefully estimating each “C,” businesses can make more informed decisions.
1. Character
Character reflects a client’s financial reputation and track record. Through bureaus like Equifax, D&B, and Experian, businesses assess their customers’ past bankruptcies, unpaid liabilities, payment history, or any legal judgments. A stable financial condition and a robust credit background make a client less risky and more reliable.
2. Capacity
Capacity helps to understand whether a customer will be able to repay the supplier. Credit teams assess repayment capacity through trade references, bank data, and cash flow analysis, checking a client’s cash flow stability, and following financial news about them to comprehend their financial position.
3. Collateral
Collateral refers to assets a borrower offers as security for a loan, similar to a mortgage. Offering collateral can improve the chance of securing a larger credit line while giving the credit team greater confidence. Lenders often require high-risk clients to provide collateral to reduce potential losses
4. Capital
Capital represents the financial resources a client possesses, such as assets and equity. Credit teams estimate public financial statements to determine these assets, including both financial and non-financial resources. The higher the amount of capital, the more security is provided to a lender, as these assets can be used if a customer defaults, which mitigates a loan’s risk.
5. Conditions
These involve not only various customer’s financial metrics, such as cash flow, statements, income reports, and balance sheets, but also broader economic ones like industry trends and geopolitical situations. These factors play a vital role in establishing the terms and cost of credit.
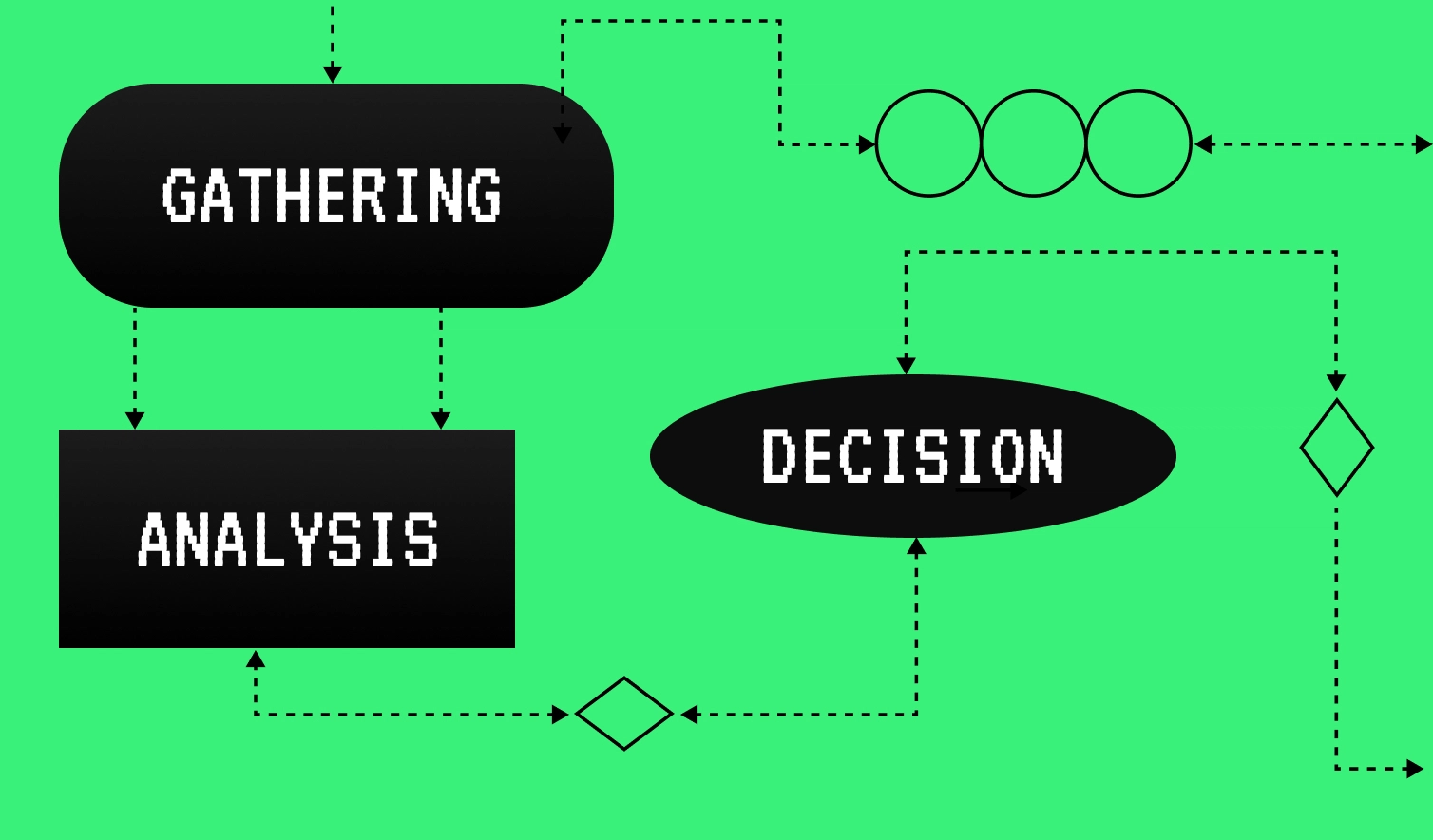
3 Key Stages of the Credit Decisioning Process
The credit decisioning process is a complex and data-driven journey that requires accuracy and consistency. While it can be broken down into many smaller steps, we're going to answer the question of what are the three core stages of the credit decision process that define its success.

Information Gathering
At the beginning of the work process, the credit team gathers all the necessary information about a client and verifies its accuracy. This includes all the information needed to prove a customer’s credit reliability, such as financial statements, private data (KYC or transactional data), credit reports, and other documentation, as well as alternative data, which we’ll discuss further.
Information Analysis
During this stage, the team analyzes the gathered data to evaluate the applicant’s credit risk. There are different methods lenders use to estimate a client’s willingness and ability to repay the loan. Here are some of the most popular and efficient ones:
Financial ratio analysis
This method focuses on examining an applicant’s financial statements (income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow reports), to assess their solvency, profitability, and liquidity. By analyzing ratios such as the debt-to-income ratio or current ratio, lenders gain a clearer view of how efficiently a borrower manages debt and whether they have sufficient cash flow to service it.
Economic condition analysis
This component of risk assessment considers the broader economic environment and its potential impact on a borrower’s ability to repay the loan.
Factors such as inflation rates, employment levels, and industry performance can significantly influence a client’s financial resilience. With such data at hand, lenders can adjust their credit decisioning models, set appropriate risk thresholds, and maintain portfolio stability across changing conditions.
Credit scoring
The assessment of financial background, along with other factors, produces a credit score that indicates lending risk. There are different ways how credit scoring can be done, such as referring to credit bureaus or using artificial intelligence and machine learning to build and retrain a decisioning model, giving solid background for a well-informed credit decision-making process.
Collateral evaluation
When applicable, lenders also assess the value and reliability of assets proposed as collateral. This involves estimating the collateral current market worth, liquidity, and potential depreciation over time. A thorough collateral evaluation not only serves the lender’s interests but can also lead to more flexible and competitive loan terms for the borrower.
Decision-Making
Based on the results of information gathering, a lender decides to either grant approval for a credit suggestion, reject it, or approve it with modified terms, for example, a lower credit limit or a higher interest rate.
All these stages allow lenders to leverage intelligence for effective decision-making, mitigate risk exposure, and ensure ethical lending practices.
Major Credit Decisioning Challenges
As an essential component of the financial industry, a proper credit decisioning process may bring businesses impressive results. However, achieving this is not a simple task. Credit teams should be very attentive and expert at their work to do so. Here are some typical credit decisioning challenges companies may face during the process:
Outdated Models
It’s crucial to constantly update your company’s legacy systems, whether these are scoring engines or data infrastructure, as old credit decisioning software usually struggles to adapt to customer behavior or changing economic conditions.
Solution:
Adopting automated or AI-driven tools for credit decisions can help modernize the whole process. For instance, platforms like GiniMachine enable lenders to automatically build and update scoring models based on fresh data, removing the need for manual recalibration. This keeps the decisioning model flexible, transparent, and responsive to real-world trends.
Poor Integration With Digital Channels
Even with automation in place, lenders often struggle to ensure its smooth integration across systems.
Solution:
If you prefer to avoid stitching multiple vendors, an end-to-end lending platform like HES LoanBox, where all the user journey is within one solution, can reduce integration friction and speed time-to-market. Otherwise, make sure each functional module you integrate into the system (for instance, for digital onboarding or loan origination), connects seamlessly with others and doesn’t disrupt existing workflows.
Limited Data Sources
Timely and accurate data nowadays is the most precious resource any company may have. However, it’s important to pay attention not only to data quality but also to its amount. Times change, and nowadays if businesses face clients with thin or non-traditional credit files, the information from the traditional credit bureau or the one provided by a client may not be enough.
Solution:
Lenders can additionally use a scope of data sources beyond the information provided directly by the customer. These may include shared data accessed through open banking and other external sources like tax records, utility, and telecom payment histories. A relatively new and not yet widely adopted solution that can be highly effective for certain industries and regions is using alternative data. Social, behavioral, or geolocation insights can help evaluate applicants who have thin or non-traditional credit files.
Manual Overrides
The automation of credit decisioning has become one of the most promising finance trends in 2025, and for a reason. Still, many institutions rely heavily on manual input from underwriters. Too many manually managed tasks often cause inconsistency, slower processing, and subjective credit decision-making. Tracing or auditing the logic behind approvals and rejections might come as an extra difficulty.
Solution:
Introduce hybrid decisioning frameworks, where automated systems handle the majority of routine cases, and human experts only review exceptions or borderline applications. Over time, data from manual overrides can also be used to retrain and refine your automated models.
Bias and Fairness Issues
Data bias remains one of the most sensitive and complex challenges in credit decisioning. If left unchecked, bias not only damages the lenders' reputation but can also expose institutions to legal risks.
Solution:
Implement explainable AI (XAI) and monitoring tools that make decision-making transparent. Regularly validate datasets for bias and retrain models using balanced and representative data. Involving compliance experts and diverse teams in model validation can also make your decisioning process more ethical and fair to all applicants.
Regulatory Compliance Gaps
As a provider of credit solutions, we regularly face cases when a client has a nontransparent credit decision-making process. Important to note, this approach is becoming riskier each year, as regulatory requirements like ECOA, GDPR, and FCRA are getting stricter and more widespread.
Solution:
To prevent legal or reputational problems, adopt transparent and auditable credit decisioning systems that record how each decision is made, what data is used, and why. Establish internal workflows that align with regional regulations, and run regular audits to verify if they still adhere. Alternatively, you could collaborate with technology partners who comprehend the legal landscape and utilize their expertise.
How to Streamline Your Credit Decision Making Process
Sometimes the decision-making process can lead to numerous credit challenges, but it doesn’t mean it’s always like that, and it can’t be handled without them. Pay attention to these factors during your credit decisioning process, and you will be able to prevent all difficulties:
- Collect comprehensive data. Build a robust dataset with credit reports, industry insights, and financial statements from your client.
- Analyze effectively: Dive deep into financial ratios and credit scores, and other metrics to prove a customer’s credit reliability.
- Define clear terms: Set realistic payment and credit limits based on your risk model.
- Evaluate potential risks: Use payment history, borrower’s payment behavior, economic indicators, and alternative data to anticipate defaults.
- Monitor continuously: Constantly do risk monitoring by checking the customer’s payment behavior and financial health after extending credit to spot warning signs early.
How We Appoach This
When modernizing credit decisioning for customers, the HES FinTech team typically focuses on architectural flexibility rather than individual tools, building configurable decisioning flows that can evolve over time as requirements change (with integrating scoring models and alternative data sources). This becomes feasible with a modular architecture, such as the one behind HES LoanBox.
Conclusion
At first glance, credit decisioning may seem complex, but with the right tools and processes, it becomes a reliable growth engine for your business.
As a trusted provider of automated decisioning solutions, we help lenders modernize their credit operations and make faster and fairer lending decisions.